Planning in India and Germany
For successful implementation of water infrastructure projects, it cannot be over emphasized that these complex water infrastructure projects should be well planned. In this context, one is interested in assessing the planning process that is traditionally being practiced in India, by comparing it with the planning practice in Germany. Such a study brought out the strengths and limitations of existing planning processes, and what changes one needs to make before transferring planning procedures from one country to the other or before developing planning and design tools, e.g. K++, for both countries. Not only technical but also social, economic and environmental conditions prevailing in India and Germany were considered. 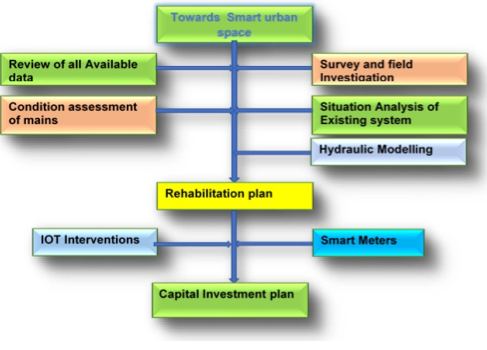

While the overall goals of planning do not differ significantly, subtle differences in planning and design processes in India and Germany exist because of (i) data availability and difficulties in collection of baseline data, (ii) approach to the concept of “design life”, (iii) water availability, and its spatial and temporal variation, (iv) differences in standards, (v) engagement with stakeholders and (vi) differences in the perception of “smart cities” concept. A report has been prepared in this regard. This report is based on a study of several “detailed project reports (DPRs)” prepared earlier, discussions with consultants engaged in planning process and brainstorming sessions with public utility organizations such as Chennai Metro Water Supply and Sewerage Board (CMWSSB), Tamil Nadu Water Supply and Drainage (TWAD) Board etc. The input of German experiences was taken from the experiences of the project team as well as from discussions with German water system operators and approving authorities.